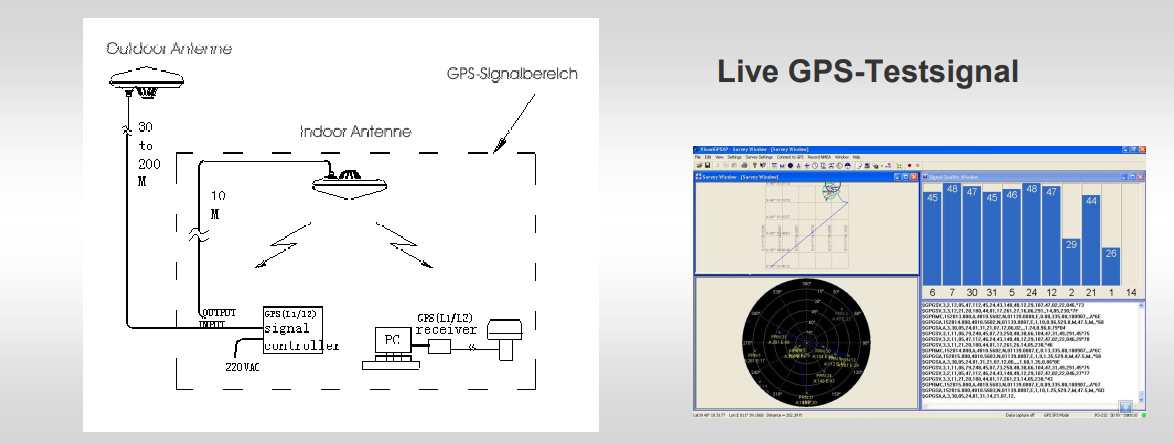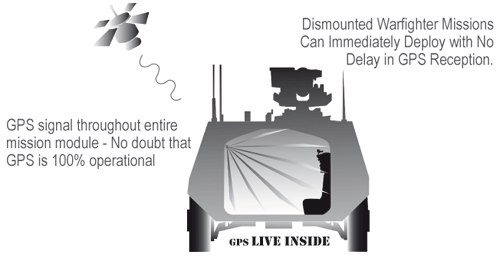
As partner of GPS Source/USA, we offer complete repeater systems, specified according to MIL standards, suited for varius military purposes, which ensure a continuous and flawless GPS reception in e.g. halls/buildings, aircrafts or vehicles of all kind. This provides for an instant readiness of the navigation system, e.g. at quick-response starts of airplanes. Also for troop transports, a steady GPS reception is very important, especially in the scope of equipment renewal for the infantry (IdZ – ES, or NATO Soldier Modernization for other NATO partners), as it supplies the soldiers with instant orientation when jumping off transport or combat vehicles auch as the Boxer, Dingo or Puma. The oftentimes lengthy acquisioning process for a valid GPS signal (L1/L27L5) can be omitted, the GPS signal is instantly available. Same applies for parachutists with NavAid Receivers, who jump off transport planes. Several Boeing C-17 Globemaster machines have been successfully equipped with this specially adapted system. For the Airbus A400M, a kit is already being tested.
The main advantages are:
- Eliminates the often lengthy acquisioning process for a valid GPS signal (Time To First Fix- TTFF)
- Exact knowledge of the position at any time, especially during transport or on jump-off
- Continuous availability of valid positioning data, e.g. for radio, locating and navigation
- Repeatedly battle-tested technology
- Longer operating times of GPS handhelds due to lower power imput during tracking
Download pdf-file GPS-Repeater for armoured vehicles/ Eurosatory 2010(900 kB)
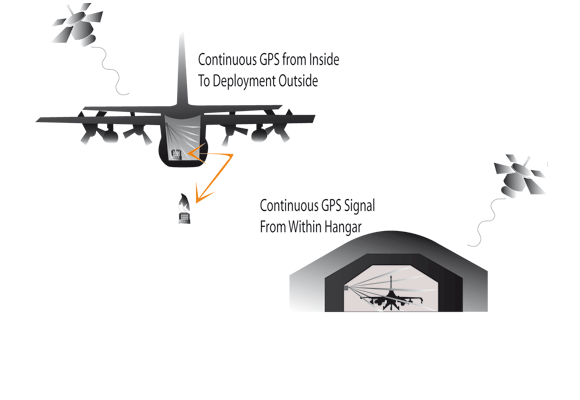
Together with our US-American partner GPS Source, ione of the biggest producers for GPS signal distribution, we develop, adapt and integrate GPS repeater solutions for branch- and customer-specific GPS applications both for military and civil use.
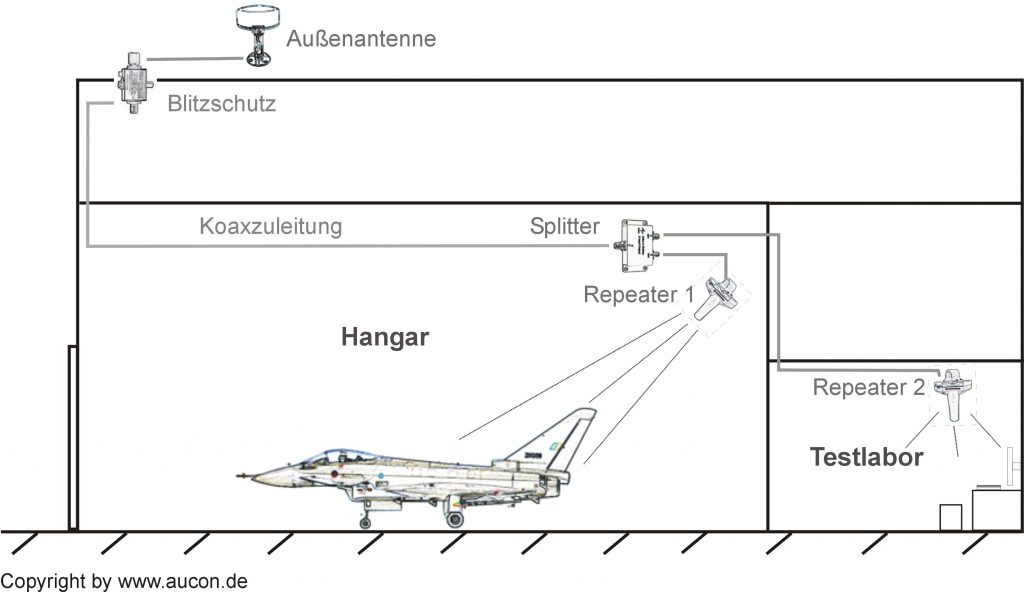
For over 10 years, AuCon has been focussing on GPS systems for signal distribution to optimise process flows in production halls, workshops and laboratories. In the fields of civil and military aviation, the reception of GPS signals in hangars or workshops can contribute to substantial cost savings and additional safety. The avionics can be easily tested inside the hangar, without having to move the aircraft outside the hall. Just recently AuCon won the tender to equip all aircraft shelters at the NATO airfield in Neuburg/Donau and is thus contributing to fighter jets such as the Eurofighter and the Tornado being able to take off in navigation mode more quickly, due to a constant GPS reception.
If you require a valid LIVE GPS signal in a vehicle or a hall, please contact us for more information.
Your personal contact for MIL applications:
Mr. Willi Fink
E-Mail: vertrieb@aucon.de
See a pattern for a signal distribution in a hangar(400 kB)
AuCon references at Bundeswehr:
JG 74 Neuburg, JaboG 31 Nörvenich, JG71 Richthofen, Heeresflugplatz Rheine-Bentlage, Fliegerhorst Faßberg, Fliegerhorst Jagel, Flugplatz Niederstetten, Görmarkaserne, TU Freyung u.v.a.
Press reports:
Wehrtechnik 2010, MIL-Tech, Strategie & Technik, German Army Armament 2010, Wehrtechnik 2012
AuCon references in the field of security and defence:
RUAG, Cassidian, Eurocopter, EADS Defence & Security, EADS Military Air Systems, Krauss-Maffei-Wegmann, Rheinmetall Defence and more
In some cases, we can give you more detailed information on reference projects upon personal request.
Exhibitions 2012: Eurosatory/Paris
We will offer trainings and information events on GPS simulation, GPS test engeneering and on measures against GPS jamming, GPS spoofing and GPS faking, shortly.
New products and developments in 2013: GNSS AntiJamming, phased array antennas, GPS signal generators and simulators.
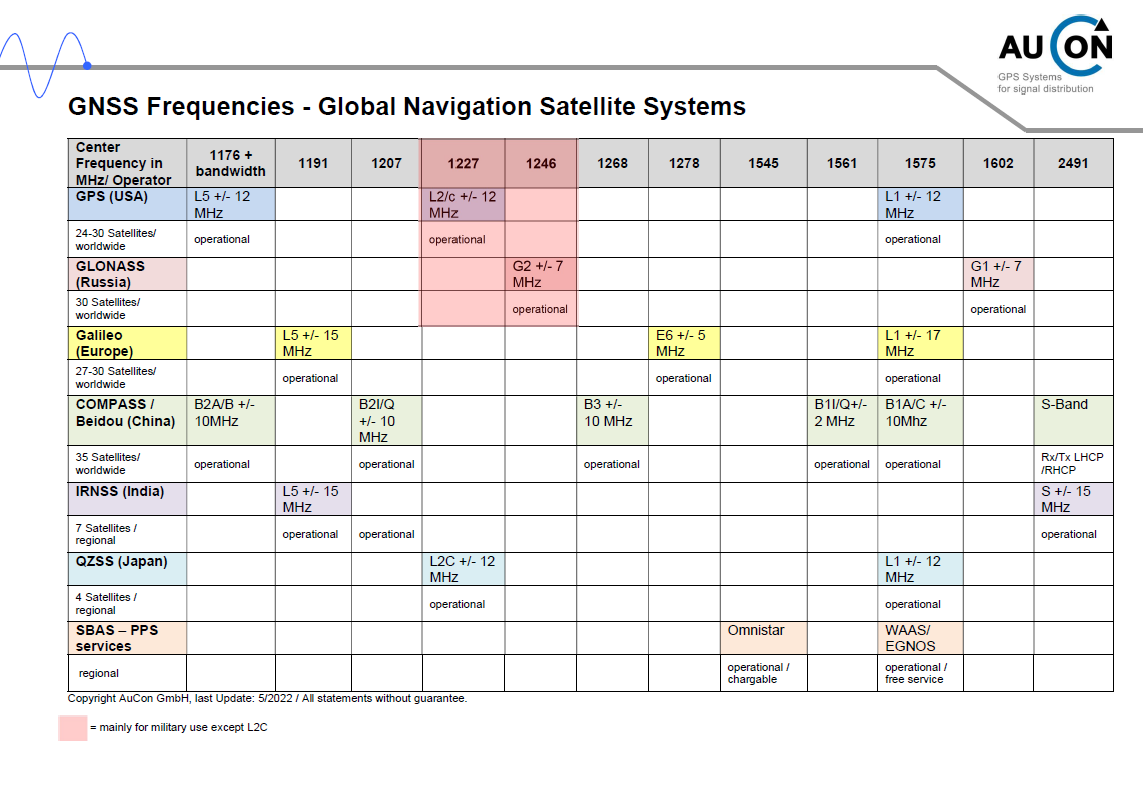


 The Federal Office of the Bundeswehr for Information Management and Information Technology has granted us the general permission to set up GPS repeaters on Bundeswehr premises. As a certified partner, we supervise the installation of components, issue installation records based on the ETSI
The Federal Office of the Bundeswehr for Information Management and Information Technology has granted us the general permission to set up GPS repeaters on Bundeswehr premises. As a certified partner, we supervise the installation of components, issue installation records based on the ETSI